Predictive Maintenance (PdM) has moved from buzzword to proven strategy. It has revolutionized how production plants manage asset reliability, but every advantage comes with a trade-off. The real question is: do the pros outweigh the cons for your operations?
PdM leverages asset health data collected through modern sensors and IoT devices (e.g., wireless vibration monitoring sensors). Advanced analytics and AI turn that data into insights, highlighting emerging issues, likely root causes, and recommended maintenance actions. By turning complex data streams into clear guidance, these reports enable maintenance teams to act before failures occur.
With a Predictive Maintenance platform, insights become operational efficiency: interventions are aligned with production schedules, spare parts and staff can be pre-staged, and costly unplanned outages are avoided.
Adopting a Predictive Maintenance strategy allows maintenance teams to anticipate failures and intervene at the optimal moment, before performance drifts or equipment breakdowns, a clear advantage over a reactive approach. At I-care, our clients have already seen the difference. On average, they achieve a global uptime increase, and critical production losses are avoided every 17 minutes.
This article explores the pros and cons of PdM, highlighting its benefits in terms of uptime, costs, safety, and sustainability, as well as the challenges associated with investment, technical complexity, and implementation, and also mentions Predictive Maintenance services that support these outcomes in practice. Real-world examples and industry data provide evidence of how these advantages can be achieved and where the limitations need to be managed.
Before diving deeper, here’s a snapshot of the key advantages and disadvantages of PdM you’ll find explored in detail throughout this article:
- Advantages: increased uptime, lowered total maintenance costs, increased asset lifespan, uplifted Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), strengthened safety, streamlined regulatory compliance, improved energy efficiency and sustainability, and enabled data-driven continuous improvement in maintenance practices and asset reliability.
- Disadvantages: upfront investments, technical complexity and skill gaps, cybersecurity, and data governance risks.

Table of Contents
Predictive Maintenance in Brief
Predictive maintenance (PdM) is a maintenance strategy that analyzes historical and live machine health data, using inputs such as vibration, temperature, or oil analysis, to predict when equipment will fail. It allows maintenance operations to be performed just in time: before a run-to-failure breakdown occurs, and more efficiently than calendar-based Preventive Maintenance (PM).
PdM combines condition monitoring techniques such as vibration analysis, thermography, or oil analysis, relying on handheld instruments for spot checks, portable data collectors for route-based inspections, and IoT sensors that stream data in real-time. These inputs are then processed through advanced analytics and machine learning, and connected with systems such as CMMS or EAM to transform insights into actionable steps.
Together, this ecosystem enables teams to base interventions on actual risk and condition, ensuring that maintenance is optimized for reliability and efficiency.
PdM sits within a broader spectrum of maintenance strategies, each with its own approach to timing interventions. Understanding these approaches helps clarify how Predictive Maintenance differs from and complements other methods:
- Preventive maintenance (interval-based): maintenance is scheduled at fixed intervals regardless of actual condition. Simple, but prone to over- or under-maintenance.
- Condition-based maintenance (threshold-based): maintenance is triggered once a parameter exceeds a defined limit, reacting to observed deterioration.
- Predictive maintenance (trend-based): maintenance is planned by analyzing multivariate patterns and trends across multiple signals and histories, often before thresholds are breached. Learn more about Predictive Maintenance
- Prescriptive maintenance (recommendation-based): maintenance decisions are guided by advanced AI and simulation models that not only predict failure but also recommend or automate the optimal corrective action, balancing cost, risk, and performance.
Key Advantages of Predictive Maintenance
What are the key benefits of Predictive Maintenance? In practice, PdM shifts maintenance from reactive firefighting to proactive planning, delivering measurable gains in uptime, cost, safety, and more.

These benefits can be grouped into eight main categories:
- Increased Uptime
- Lowered Total Maintenance Costs
- Increased Asset Lifespan
- Uplifted OEE
- Strengthened Safety
- Streamlined Compliance
- Improved Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
- Enabled Data-driven Continuous Improvement
Increased Uptime
One of the most visible benefits of Predictive Maintenance is its positive impact on asset uptime. By detecting subtle deviations in machine health early, PdM identifies potential issues before they escalate, preventing breakdowns and the unplanned stops they cause, while allowing teams to schedule the intervention during planned stops to avoid costly downtime.
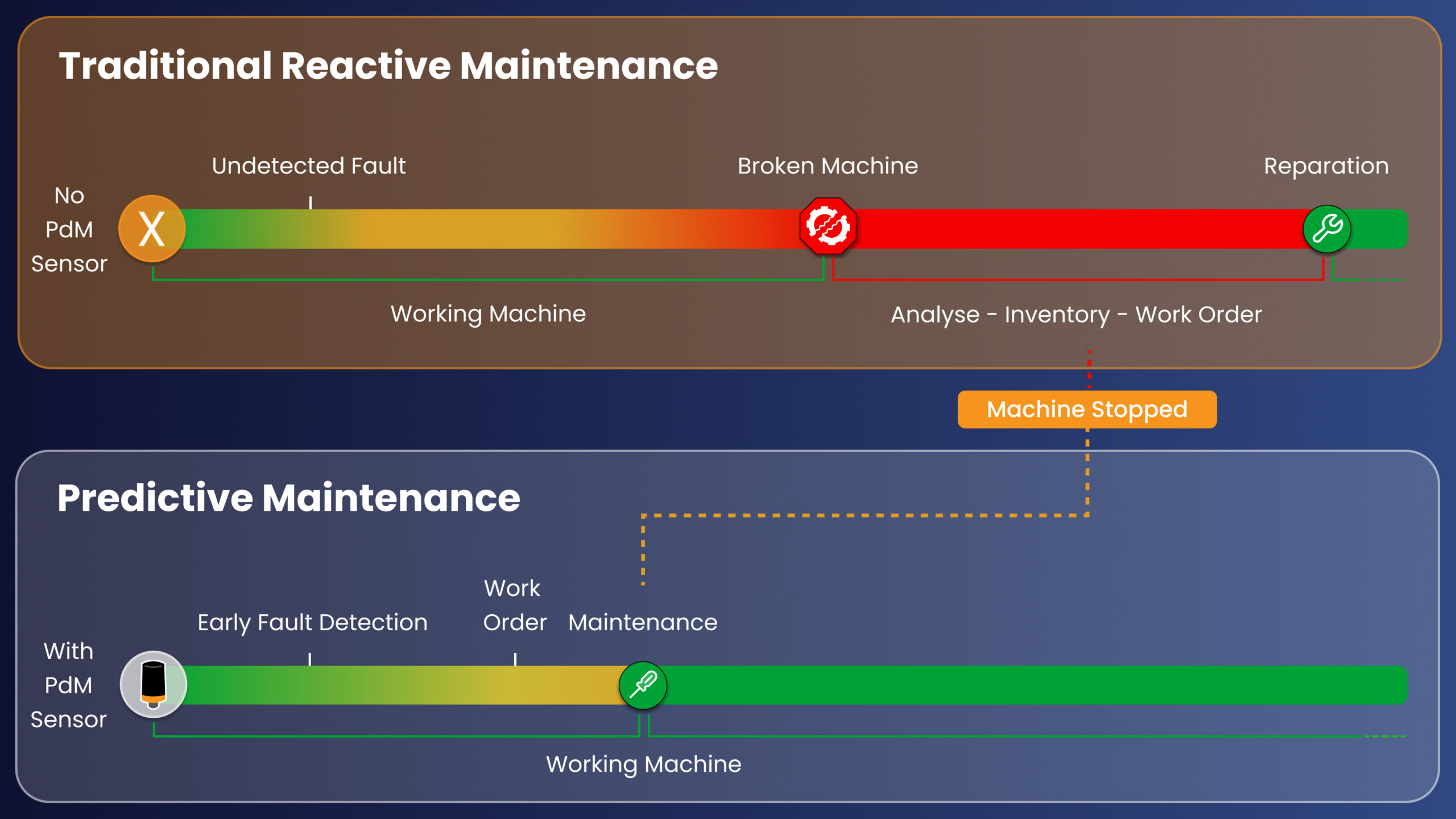
Better Uptime is achieved through:
- Prevention of collateral failure by catching the issue early
- Avoidance of premature or delayed maintenance actions
- Scheduling of maintenance during low-load production windows
- Pre-staging of spare parts and staff before interventions
- Data-driven root-cause analysis to stop repeat failures and reduce unplanned repairs
- Stabilization of production planning for greater predictability
This shift results in a longer Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF), which indicates greater asset reliability, and a shorter Mean Time To Repair (MTTR), which measures the speed of repairs.
Independent research confirms this benefit. Companies that implement PdM successfully achieve 35–50% reduced downtime, directly protecting production output and revenue.
Real-World Example
At a large wind farm, vibration analysis sensors flagged early-stage wear within a turbine gearbox, long before any damage was detectable by operators. Thanks to PdM insights, technicians scheduled the repair during a forecasted low-wind window. The intervention prevented an unscheduled call-out, avoided last-minute crane mobilization, and safeguarded electricity production that would otherwise have been lost.

Lowered Total Maintenance Costs
Another major advantage of Predictive Maintenance is its ability to control and reduce maintenance costs. By detecting issues early and accurately forecasting failure timelines, Predictive Maintenance helps organizations optimize maintenance execution and eliminate wasteful spending.

Reduced Total Maintenance Costs are achieved through:
- Elimination of overtime labor premiums
- Avoidance of express freight and unnecessary contractor mobilizations
- Leaner spare-parts inventory and fewer stock-outs
- Reduction of penalties tied to missed production targets
- Stabilization of cash flow with planned work
This optimized execution makes maintenance spending more efficient, reducing overall Total Cost of Ownership (TCO).
McKinsey estimates that digitally enabled reliability programs, including predictive maintenance, can reduce maintenance costs by 18-25%.
Real-World Example
At a major brewery, vibration and temperature analytics on a rotary filler’s drive bearing flagged degradation two months before any visible signs. The maintenance team replaced the bearing during a nightly sanitation routine, avoiding costly emergency premiums and rush freight.

Increased Asset Lifespan
Predictive Maintenance not only reduces downtime and costs, but it also helps assets last longer. By combining diverse asset-health inputs, including sensor data, operational logs, manual inspections, and historical maintenance records, Predictive Maintenance detects early degradation trends, prevents catastrophic failures, and slows progressive wear.
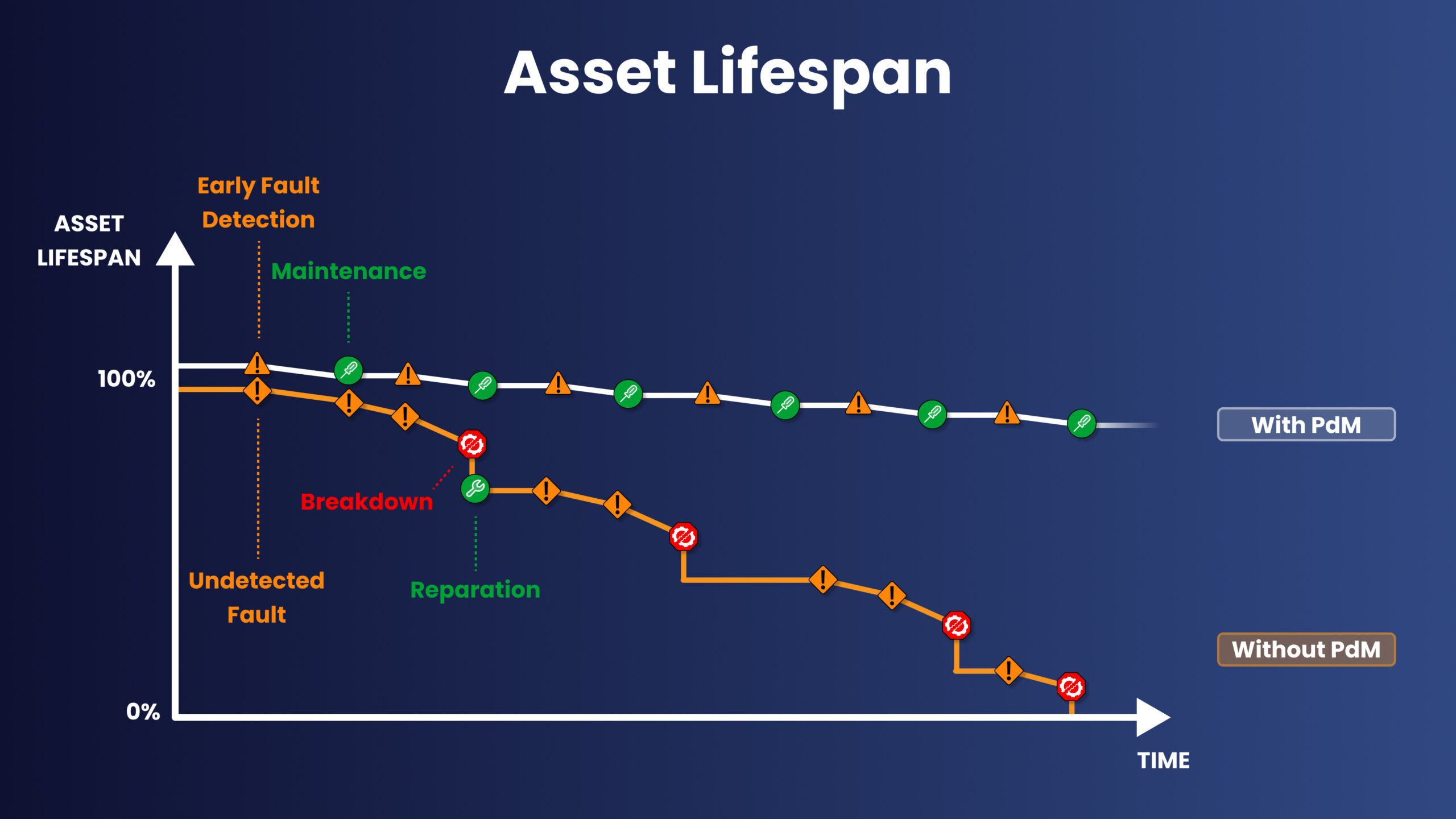
Improved asset lifespan is achieved through:
- Optimization of lubrication schedules to minimize premature wear
- Optimization of operational loads to reduce stress on components
- Integration of failure-mode feedback loops into PdM technologies for continuous learning
- Streamlining of overhaul intervals for greater efficiency
- Reliable RUL forecasts that defer major capital equipment purchases
These benefits are reflected in extended Remaining Useful Life (RUL), fewer run-to-failure events, deferred capital expenditures, and the potential for a higher Return On Assets (ROA).
A large-scale PwC survey of 268 manufacturers found that those adopting PdM extended asset lifetime by an average of 20%.
Real-World Example
At an offshore oil platform, predictive vibration monitoring on a seawater-injection pump flagged emerging shaft misalignment before performance declined. Maintenance crews realigned the pump during a scheduled well test pause, protecting equipment uptime and extending the pump’s longevity by several years.

Uplifted Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Predictive Maintenance has a direct impact on Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), the benchmark metric for manufacturing that combines three pillars: Availability, Performance, and Quality. By improving all three simultaneously, PdM raises equipment efficiency, strengthens production continuity, and boosts overall plant performance. In practice, this translates into higher throughput, better product quality, fewer disruptions, and stronger revenue streams.
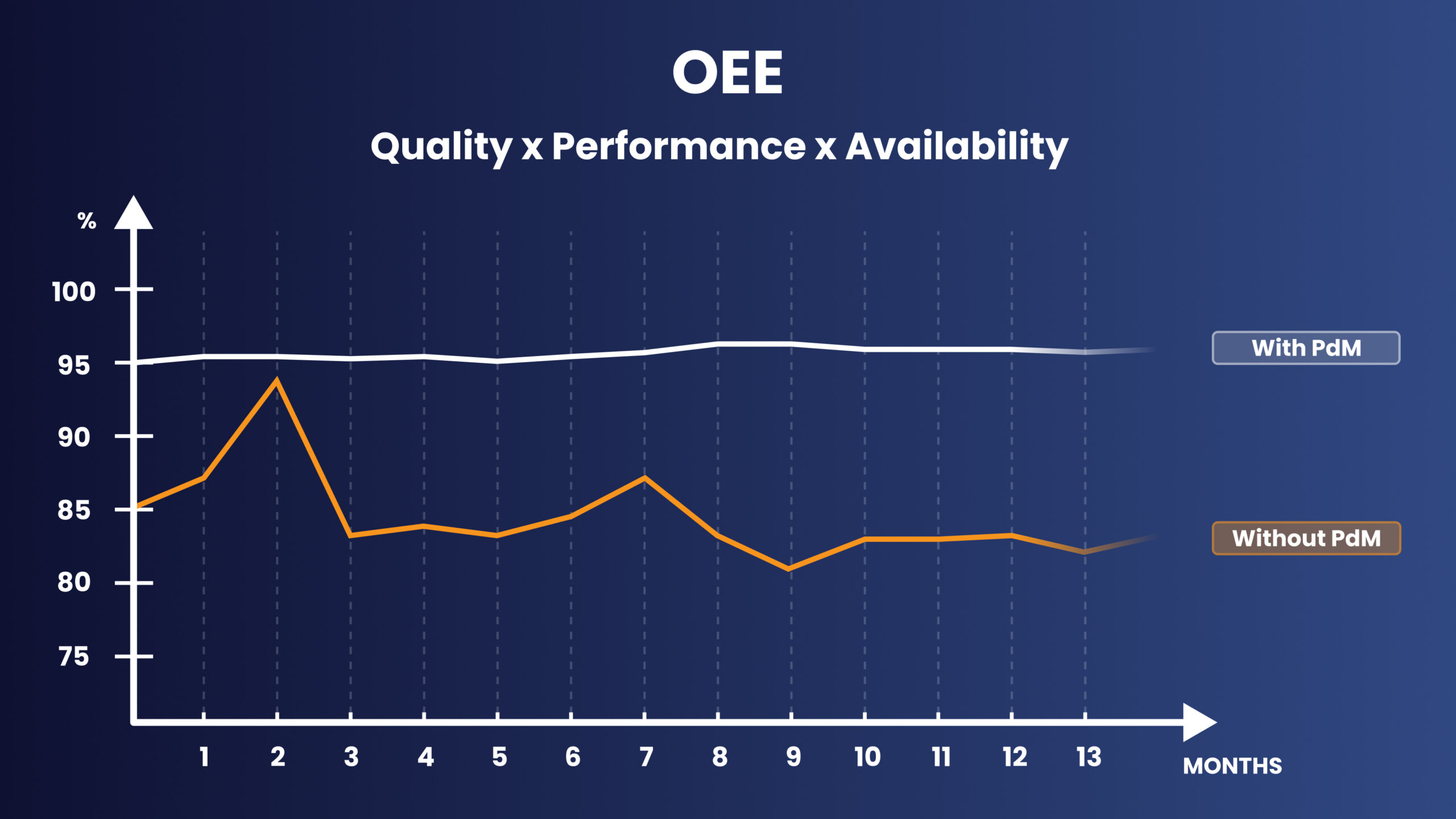
Improved OEE is achieved through:
- Reduction of unplanned stoppages by catching faults early (Availability)
- Stabilization of production cycles by eliminating micro-stops and slowdowns (Performance)
- Lower scrap and rework rates through earlier defect detection (Quality)
- Continuous tracking of the Six Big Losses to guide performance improvements
Real-World Example
On a high-speed beverage bottling lane, vibration analytics on a seamer motor flagged bearing wear well before operators noticed any failure. By replacing the bearings during a scheduled cleaning stop, the team not only avoided unplanned downtime (Availability) but also stabilized seaming speeds (Performance) and reduced off-spec cans caused by improper closure (Quality).
Strengthened Safety
Predictive Maintenance is not only about efficiency and cost reduction, but it also plays a critical role in safety. By leveraging real-time risk insights from sensor data, inspection logs, incident histories, and environmental monitoring, PdM helps identify hazards and failure threats before they escalate. These improvements are reflected in fewer recordable safety incidents, reduced emergency interventions, and greater workforce confidence when working around critical equipment.

Improved safety is achieved through:
- Elimination of hard-to-detect hazards, such as micro-cracks or small gas leaks
- Reduction of emergency hot-work in unsafe conditions
- Minimization of workforce exposure to hazardous environments
- Earlier lockout/tagout planning and stronger adherence to safety protocols, supported by planned work and shared data
- Standardization of incident-response workflows across teams
Companies implementing PdM report a significant benefit: a 14% average reduction in SHEQ risks (Safety, Health, Environment, Quality)..
Real-World Example
At a large chemical plant, ultrasonic gas leak detection spotted a subtle rise in flammable-vapor concentration around a solvent-storage vessel long before fixed alarms would trigger. Maintenance teams initiated a safety shutdown, purged the line, and replaced the faulty seal during a planned transfer pause. This avoided emergency hot-work, reduced personnel exposure, and prevented a potentially explosive release.

Streamlined Compliance
For many industries, compliance is as critical as productivity. By generating predictive insights from real-time asset health data, Predictive Maintenance helps identify potential risks and schedule maintenance accordingly. When integrated with connected systems, it also standardizes documentation and automatically records inspections and repairs, simplifying audits and compliance reporting.

Better compliance is achieved through:
- Creation of tamper-proof, time-stamped maintenance logs
- Automation of audit trails with electronic signatures
- Standardization of compliance documentation (ISO, OSHA, EPA, FDA…)
- Seamless integration with regulatory reporting workflows based on industry standards
- Verification and closure tracking of corrective actions
This means maintenance can be scheduled based on risk, while inspections and repairs are automatically logged and traceable. As a result, organizations face fewer audit surprises, reduce compliance-related penalties, and build stronger trust with regulators.
Real-World Example
At a large steel mill, predictive maintenance analytics highlighted early signs of machine degradation in scrubbers and cooling systems before performance drifted outside permitted thresholds. Maintenance was scheduled and fully documented in the connected CMMS, with linked work orders, inspection photos, and time stamps. When regulators conducted an unannounced audit, the team compiled a tamper-evident report combining condition-based maintenance data with digital records and workflows. The result was clear proof of risk-justified task timing, full regulatory adherence, and no notices of violation.
Improved Energy Efficiency & Sustainability
Another important benefit Predictive Maintenance offers is its impact on energy efficiency and sustainability. By guiding maintenance decisions with real-time reliability insights, PdM detects sub-optimal performance and energy waste before they escalate. These improvements are reflected in lower utility costs, reduced CO2 emissions, and measurable progress toward manufacturing sustainability and corporate ESG goals.
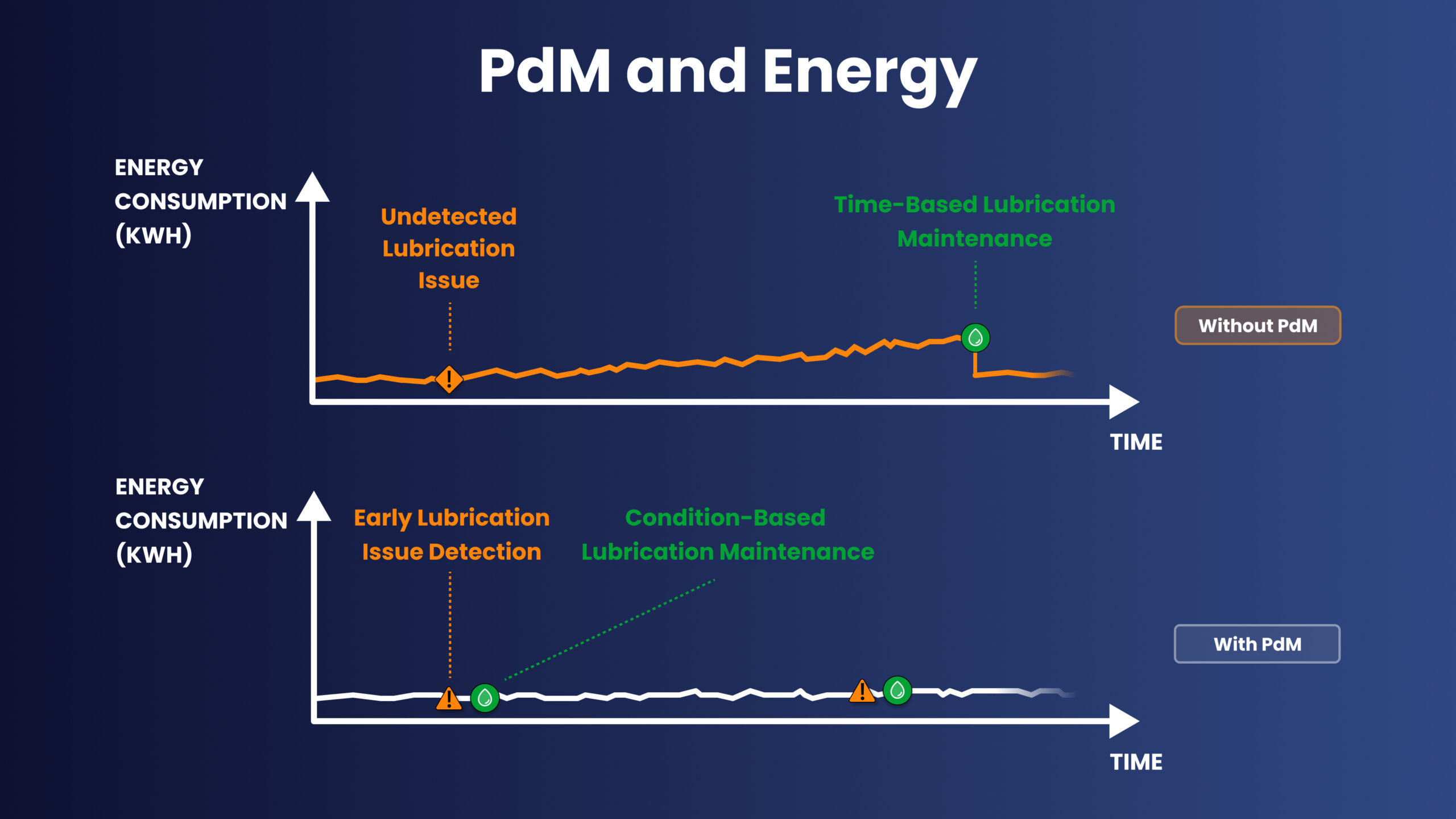
Better efficiency and sustainability are achieved through:
- Elimination of misalignment-induced energy losses
- Reduction of fouling and other efficiency drags
- Minimization of friction-related energy waste
- Avoidance of high-energy restarts after unexpected breakdowns
- Maintenance of peak asset efficiency through optimized setpoints
- Reduction of embodied CO2 emissions from emergency spare parts production and shipping
36% of PdM adopters reported energy‑savings outcomes, even though few listed energy as their primary goal.
Real-World Example
At a kraft mill, motor current and temperature analytics on a high-vacuum fan revealed rising load caused by early impeller imbalance and seal wear. Planners scheduled a balance trim and seal replacement during the next routine felt changeover, restoring the fan’s power draw to baseline and avoiding the rush shipment of a new impeller. The lower fan demand directly translated into reduced electricity consumption for the mill, leading to long-term sustainability gains, while also eliminating the embodied CO2 of manufacturing and transporting a spare component.

Enabled Data-Driven Continuous Improvement
One of the most valuable benefits of Predictive Maintenance is its ability to drive continuous improvement. By turning each anomaly alert, sensor reading, and maintenance outcome into feedback, PdM creates a loop that refines models, adjusts strategies, and ensures field performance matches planning assumptions. It also strengthens collaboration with OEMs: by aggregating asset data across plants, repeating problems can be identified and addressed, and maintenance teams can recommend the most reliable equipment for specific applications, guiding smarter asset choices in the future.
Continuous improvement is achieved through:
- Ongoing retraining and drift monitoring to keep models accurate
- Continuous adaptation of maintenance strategies as new insights emerge
- Deployment of updated workflows and processes directly in the CMMS
- Integration of field observations and PdM outcomes into a closed feedback loop
- Real-time performance feedback so teams immediately see the impact of changes
In practice, these mechanisms are consolidated into an action plan, ensuring that insights from PdM are not left as isolated learnings but transformed into specialized services, such as Reliability Engineering (REL) or Reliability-Centered Lubrication (RCL), that embed continuous improvement into day-to-day operations and support long-term performance gains.
Real-World Example
On a high-speed beverage bottling line, recurring minor overheating alerts on a conveyor drive were automatically logged and visualized on the PdM dashboard, making the pattern impossible to ignore. A reliability engineer cross-checked the alerts with past work orders and discovered the same grease point had been repeatedly skipped. The team redesigned the guard for easier access, updated the maintenance checklist, and trained operators to lubricate the point during each sanitation cycle. Follow-up readings showed the motor was running cool, the alerts had disappeared, and the improvement was permanently embedded into the process.

Key Disadvantages of Predictive Maintenance
What are the limitations and drawbacks of Predictive Maintenance? Despite its clear benefits in reliability and efficiency, PdM also brings challenges that organizations must address before or during adoption.
These include:
- Upfront Investments
- Technical Complexity & Skill Gaps
- Cybersecurity & Data Governance Risks

Upfront Investments
One of the most significant barriers to the adoption of Predictive Maintenance is the high upfront cost required to get started. Before the first savings from avoided failures are captured, companies often face sizable capital expenses for sensors, connectivity, analytics platforms, integration services, and training. For many organizations, this early burden can delay or even block implementation.
Implementation costs go well beyond the initial investment in monitoring devices. Deploying condition monitoring equipment, such as vibration or temperature sensors, may require cabling and gateways for wired installations, or additional network and IT infrastructure to handle the data flow in wireless setups.
Analytics platforms and integration services incur recurring license costs, API connection fees, and data processing charges, while resilience measures such as maintaining spare sensors in stock or setting up network failover increase capital expenditures. Additionally, skills development represents another expense, as Information Technology (IT) staff and Operational Technology (OT) teams, such as automation or controls engineers, need training to analyze data and act on PdM insights.
This barrier can be mitigated through:
- Leasing instrumentation to convert CapEx either into full OpEx (subscription), or into a hybrid expenditure combination, and so lower the initial spend
- Adopting cloud-based analytics that scale with usage, avoiding large one-time purchases
- Choosing modular, role-specific training paths that evolve with program maturity
- Subscribing to PdM as a Service bundles where sensors, software, analysts, and expert support are included for a predictable monthly fee
- Phasing deployments by asset criticality to secure early wins and demonstrate ROI
- Building TCO-based business cases to highlight lifecycle value rather than short-term payback
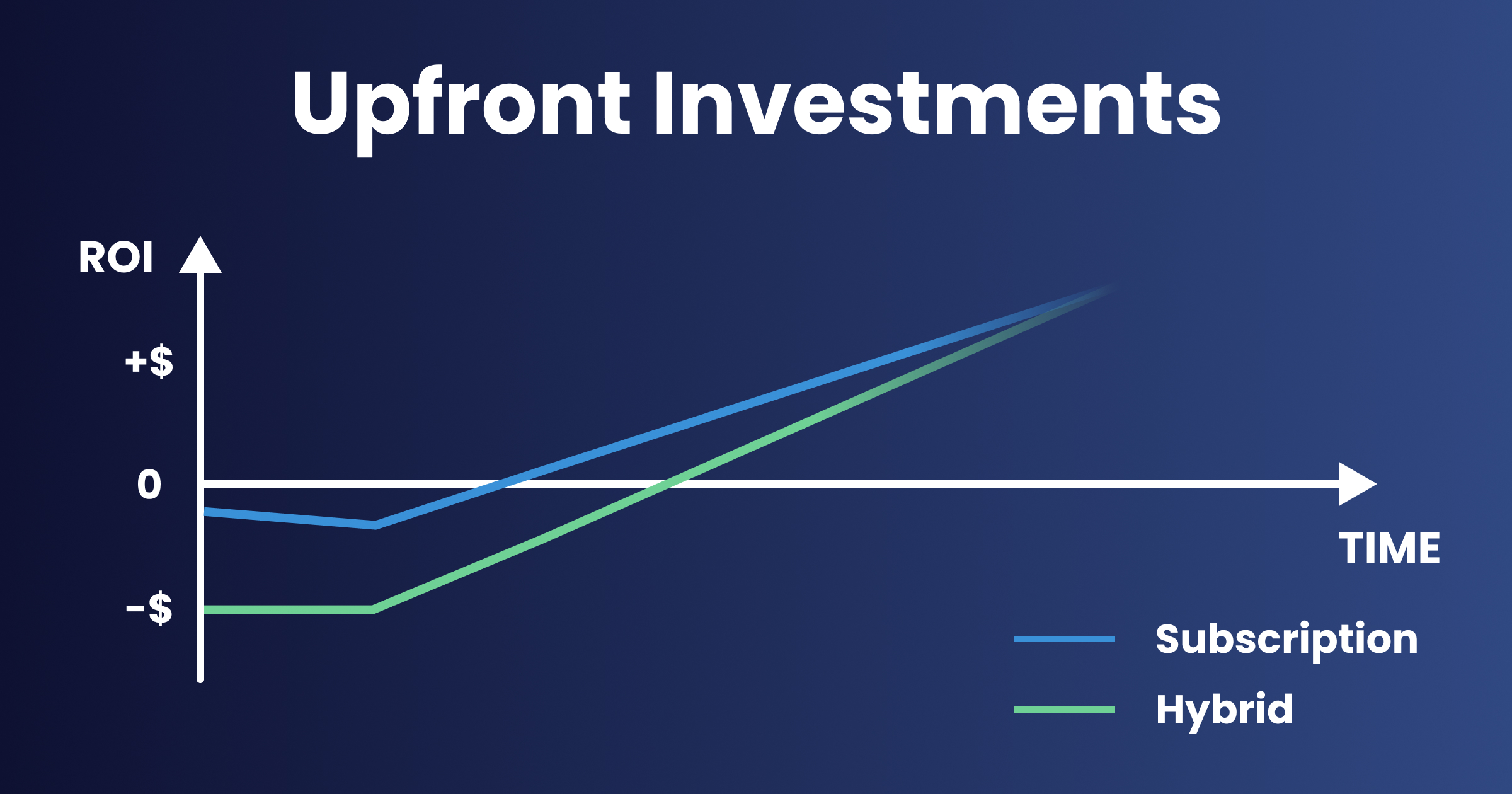
Why Buy the Hardware When You Only Need the Insights?
Upfront costs are often seen as the main obstacle to adopting Predictive Maintenance. But ownership isn’t the only path forward. Predictive Maintenance as a Service offers an alternative model, providing sensors, software, and expert analysis for a predictable monthly fee. This approach removes the need for heavy initial investments while ensuring that equipment and platforms are installed, maintained, and continuously upgraded by specialists.
Technical Complexity & Skill Gaps
Another major obstacle to the adoption of Predictive Maintenance is the technical complexity and skill gaps it creates. Unlike traditional maintenance practices, PdM requires data-science fluency, diagnostic expertise, and the ability to work with advanced technologies that many teams don’t have in-house.
In practice, very few companies manage this entirely on their own. Most rely on external companies that provide out-of-the-box models, while still requiring expert support to set up models and sensors, and interpret early results.
Once solutions are deployed, many teams lack hands-on experience with dashboards and data analysis. Alerts, thresholds, and anomaly patterns are often misread or underused, which reduces confidence in the results and slows adoption.
Adding to the challenge is the shortage of specialists in condition monitoring techniques that underpin Predictive Maintenance. Skilled vibration analysts, oil diagnosticians, and thermographers remain scarce, making it harder for organizations to unlock the full value of PdM insights.
Confidence can also be a challenge, as technicians may doubt the accuracy of AI-driven alerts when the system flags issues without clear, physical explanations. If predictive outputs are not linked to recognizable failure modes, teams can hesitate to act on them, slowing adoption.
Finally, developing new skills takes time. Conventional training is resource-intensive and often disconnected from daily operations, slowing down PdM implementation when companies are focused on near-term cost savings.
This barrier can be mitigated through:
- Rolling out targeted micro-learning modules to upskill operators, maintainers, and engineers without long absences from daily work
- Appointing cross-functional PdM champions to bridge maintenance, reliability, and data teams, ensuring insights are understood and applied
- Engaging external PdM specialists to support analytics setup and ongoing reliability coaching
- Subscribing to managed PdM service bundles that combine hardware and platform management, data science, and expert guidance under a single contract

Is Your Team Equipped to Turn Insights into Action?
Advanced analytics, sensor interpretation, and condition monitoring expertise can be hard to build internally, leaving teams unsure how to move forward. The good news is that the right training can bridge these gaps.
From foundational courses to advanced certifications, structured learning paths ensure your team can confidently deploy and sustain PdM programs. Whether in Europe or the United States, specialized programs are available to help maintenance professionals build the knowledge and confidence needed to turn predictive insights into reliable action.
Cybersecurity & Data Governance Risks
A further obstacle to the adoption of Predictive Maintenance is the cybersecurity and data governance risks it introduces. As more assets are connected and sensitive operational data flows to analytics platforms, PdM broadens the attack surface and raises sovereignty concerns, making robust protection and governance essential.
These risks stem from several sources. Each new IoT sensor, gateway, or wireless connection adds an entry point to the network, while many legacy PLCs and SCADA systems lack encryption or secure protocols, leaving data streams exposed.
Beyond technical flaws, the type of data collected can also become a liability. Detailed machine-health telemetry may indirectly reveal how a process is run or optimized. This knowledge could give outsiders or competitors an advantage if the data were exposed.
These risks can be mitigated through:
- Segmenting OT networks behind secure gateways and firewalls to isolate critical assets
- Implementing zero-trust architecture with mutual authentication and least-privilege access
- Encrypting data in motion and at rest across sensors, gateways, and cloud layers
- Masking or tokenizing sensitive data points to protect proprietary logic before transmission
- Deploying firmware-integrity controls to prevent unauthorized code changes
- Guaranteeing client ownership of PdM data and hosting it in secure, certified environments (e.g., AWS)
- Implementing backup and retention schedules with strict purge deadlines
- Establishing clear data retention and deletion policies
- Defining coordinated OT/IT incident-response plans to contain and recover from breaches
- Conducting regular security audits, penetration tests, and ISO 27001 certification to validate ongoing protection

Looking to Standardize Your Maintenance Data While Keeping It Fully Protected?
At I-care, cybersecurity is embedded into our PdM services. Our solutions are ISO 27001-certified, the global standard for information security management, which guarantees that our clients’ operational data is handled with the highest level of governance, confidentiality, and integrity.
Predictive Maintenance Pros & Cons
What are the pros and cons of Predictive Maintenance? Even if PdM delivers measurable benefits, it also introduces real challenges. Some advantages are inherent to its integration, while certain limitations require careful preparation to address.
Below is a balanced overview of the key pros and cons of Predictive Maintenance:
| Theme | Pros (Benefits) | Cons (Challenges) |
| Financial | • Lower maintenance costs • Reduced Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) • Optimized spare-parts inventory and supply chain • Fewer costly emergency repairs | • Upfront Investments in sensors, platforms, training, and infrastructure |
| Reliability | • Increased uptime • Extended asset lifespan • OEE uplift (Availability, Performance, Quality) • Faster MTTR thanks to pre-staged spare parts and planned interventions • Actionable insights for OEM feedback and smarter asset selection | • Technical Complexity & Skill Gaps, requiring AI/ML expertise, condition-monitoring specialists, and continuous training |
| Safety & Compliance | • Strengthened safety performance • Streamlined compliance and audit readiness • Early detection of hazardous conditions before escalation | • Cybersecurity & Data-governance Risks, including broader attack surfaces and data-sovereignty requirements |
| Sustainability & Strategy | • Improved energy efficiency • Lower CO2 footprint • Reduced waste and scrap through early intervention • Enabled the continuous improvement loop • Better workforce allocation: less firefighting, more strategic work | • Benefits may take time to materialize fully and require robust governance to sustain |
While these challenges are real, I-care has developed solutions to counterbalance them:
- Our Predictive Maintenance as a Service removes heavy upfront investments
- Our ISO 27001-certified cybersecurity practices safeguard operational data
Is Predictive Maintenance Right for Your Plant?
Predictive Maintenance has proven its value: higher uptime, lower costs, longer asset life, and stronger safety and compliance. Yet many plant managers hesitate, concerned about costs, technical complexity, or whether their teams are ready for PdM implementation.
PdM does not need to be adopted in one leap. It is an adaptable and effective strategy that offers a way to begin with your most critical assets and quickly demonstrate clear advantages. A single avoided machine breakdown can justify the investment, prove its cost efficiency, and lead to gradual improvements in your overall maintenance process as results are demonstrated.
Is Predictive Maintenance the right fit for your plant? Find out by contacting our team to discuss your operations and identify the maintenance solution that best matches your needs.

