Machinery Overview
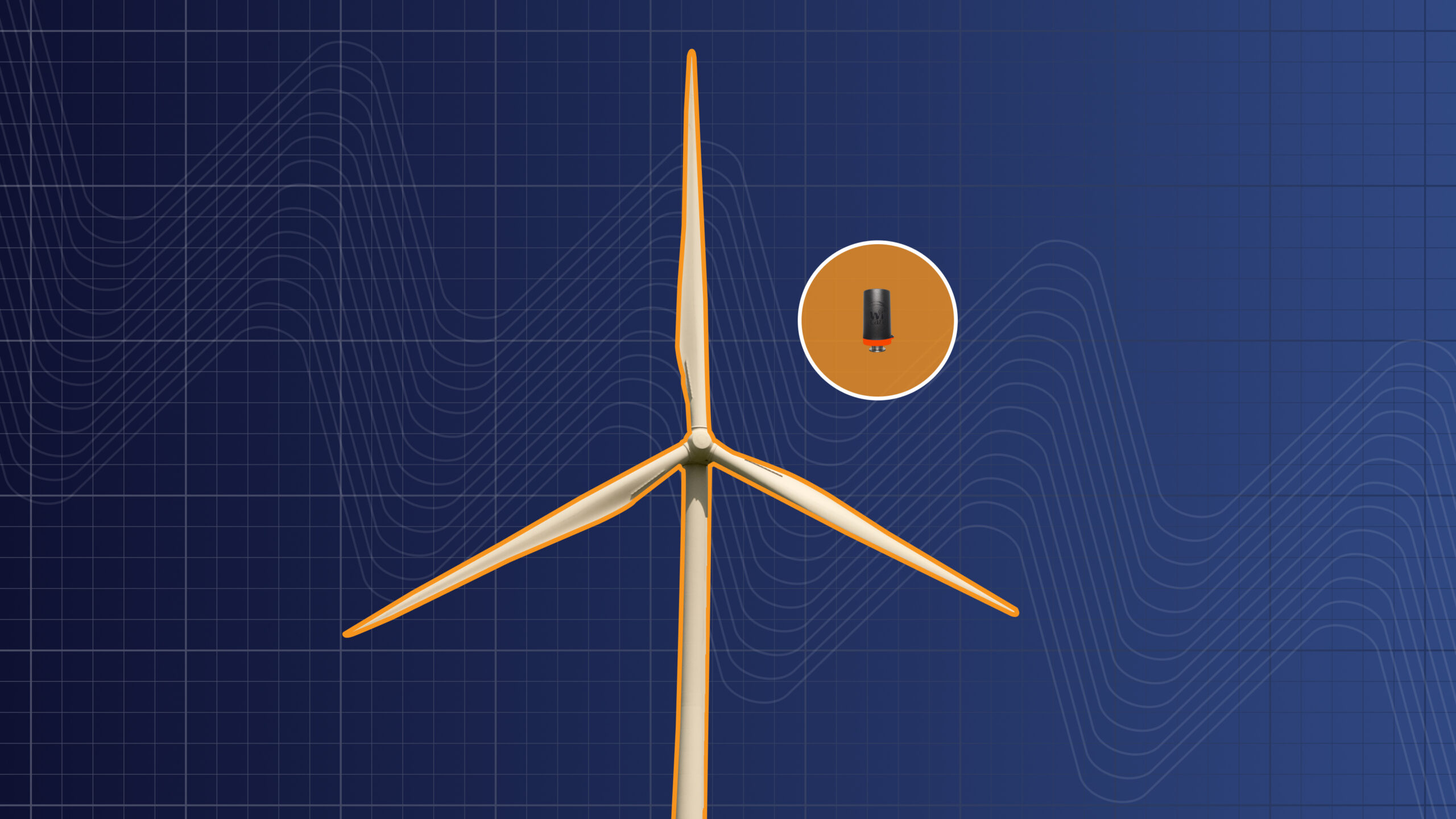
The wind turbine converts the wind’s kinetic energy into electricity. As the blades spin, they rotate the main shaft connected to the gearbox, which increases the rotation to a speed suitable for powering the generator.
Turbine power: 1.5 MW
Bearing Type: FAG 230/600
Monitoring Devices and Software Set-up
I-care reliability engineers installed Wi-care™ vibration sensors on the main rotor bearing and gearbox. These wireless sensors continuously monitor vibration and temperature, providing real-time insights into asset health.
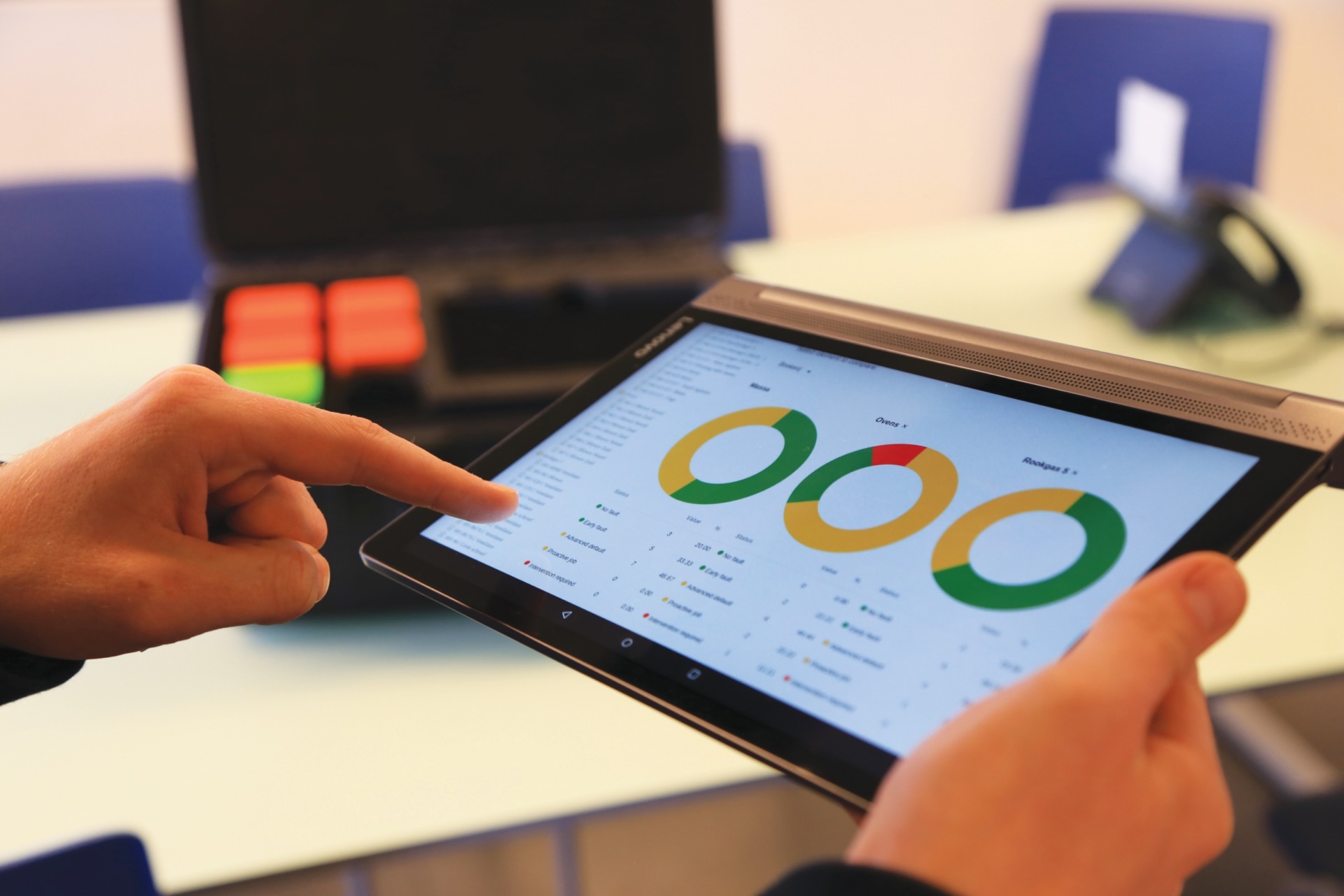
Wi-care™ sensors transmit asset data to I-see™. The AI-powered analytics platform carefully analyzes and classifies each data point to assess whether the main rotor-bearing and gearbox are operating normally, showing early warning signs, or entering a critical alarm state. AI-generated insights are transformed into clear, actionable reports that highlight evolving condition trends across the wind turbine’s key components.
I-care engineers then review these reports to conduct deeper analyses and provide actionable recommendations, as detailed in the steps below.



Detailed analysis
Step 1 | Detection of Issue
The I-see™ platform identified rising vibration levels from the main rotor bearing. Early warning signs appeared months before crossing critical thresholds, providing time to plan and act.
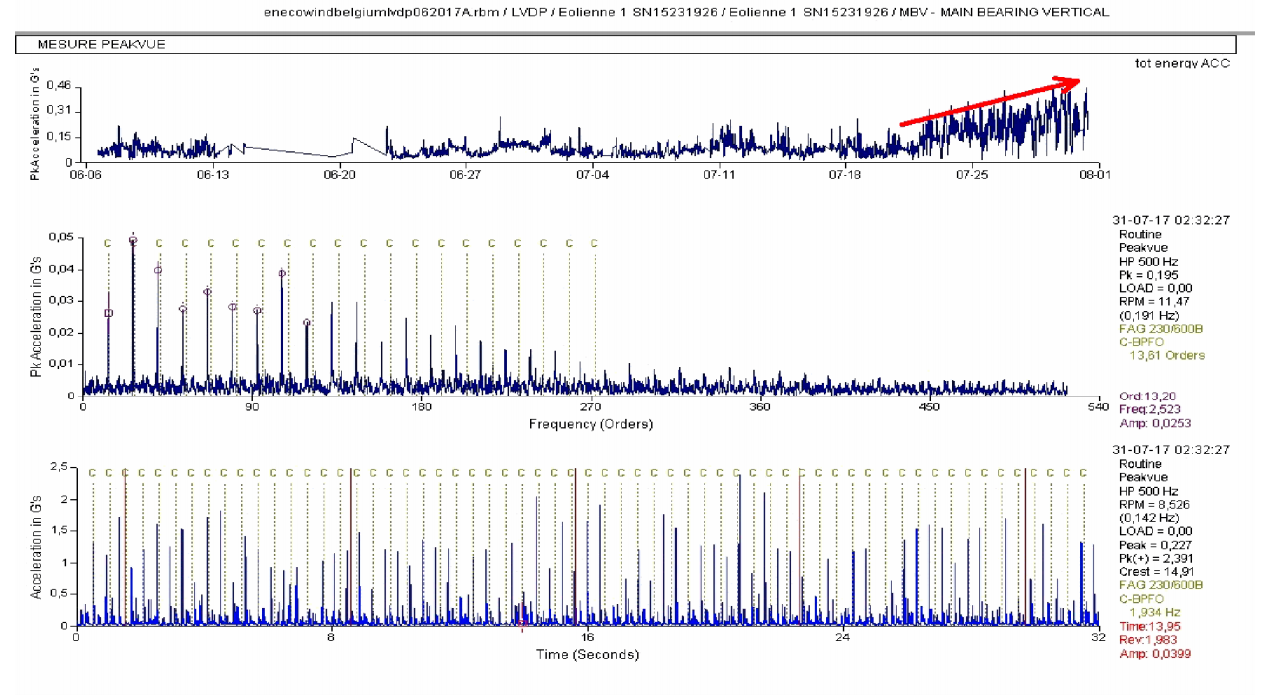
Step 2 | Analysis
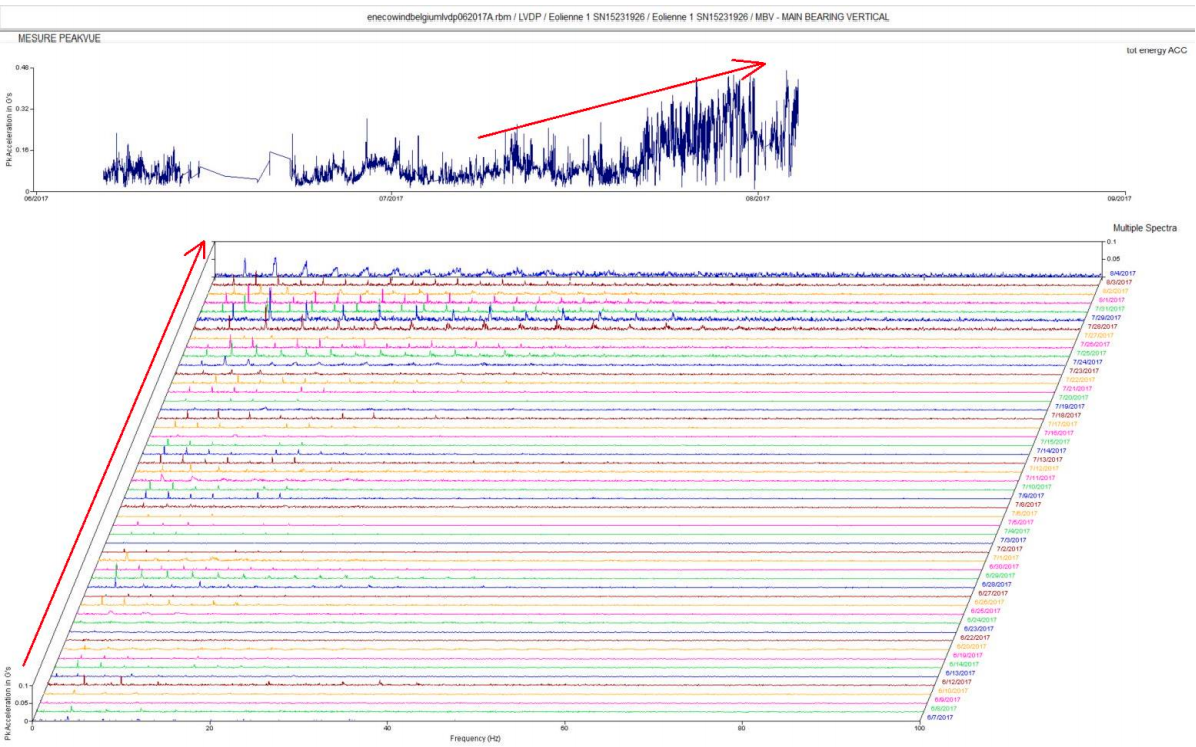
After consulting the vibration spectrum, the I-care engineer confirmed the issue and advised a grease analysis and a visual inspection.
Step 3 | Inspection
As detailed below, the grease analysis of the main rotor bearing showed elevated particle concentrations exceeding safe limits.

Because the drivetrain components are mechanically linked, a borescope inspection of the gearbox was also performed. The borescope confirmed that the gearbox had no internal damage.
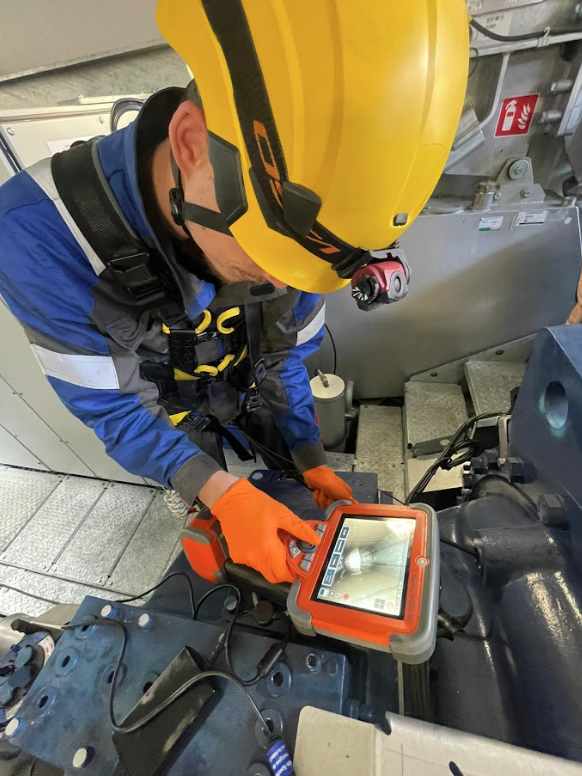

The I-care engineer recommended replacing the main bearing, a significant and costly operation, but one that would prevent damage to the gearbox.
Step 4 | Replacement
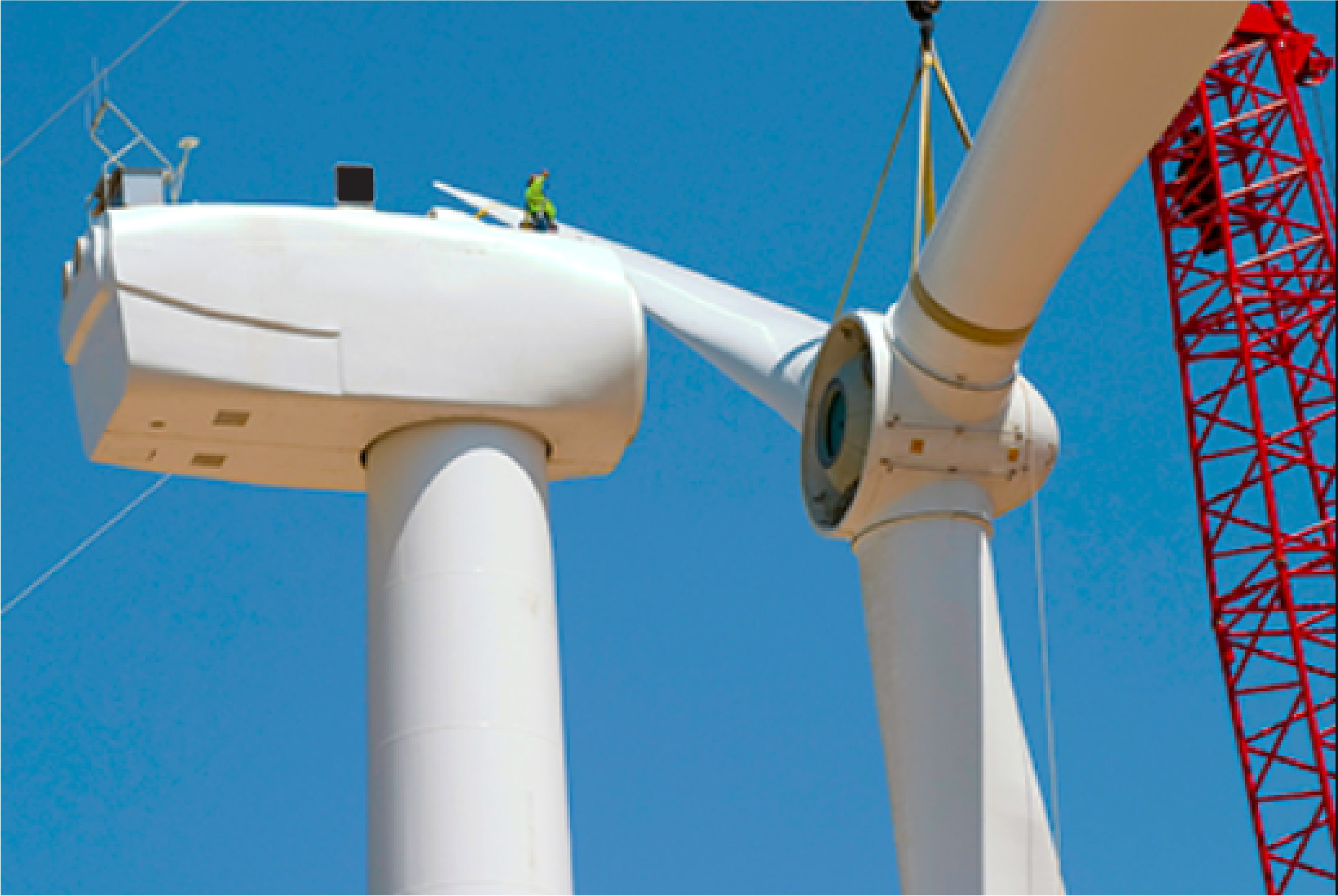
The maintenance crew carried out a swap of the main rotor bearing using a crane during the next low-windy maintenance period.

Step 5 | Further Monitoring
After replacement, ongoing surveillance ensured the main rotor bearing and gearbox remained stable and free from faults. Regular follow-ups confirmed that no further issues had arisen, supporting the intervention’s long-term success.
Results
$200,000 Gearbox Preserved Through Early Fault Detection
Without I-care’s predictive maintenance, the main rotor bearing issue could have caused severe gearbox damage, leading to unplanned downtime, costly emergency repairs, and significant production losses.
Thanks to early detection through continuous monitoring, maintenance was scheduled proactively—enabling more efficient maintenance planning across multiple turbines, reducing overall operational costs, and minimizing downtime.
Ultimately, this proactive strategy saved a $200,000 gearbox, maximized turbine availability, and supported consistent energy output.
Learn About Our
Success Stories
Our Solutions Span All Assets,
Including Yours.
Are you ready to enhance your efficiency?









